Transient keyword vs @Transient annotation
transient is a JAVA keyword (deals with serialization) whereas @Transient is a JPA annotation (deals with persistence).
We as software developers often tend to mix these topics, however these are two distinct features which can be leveraged as per business / technical requirements
Persistence) refers to the characteristic of state that outlives the process that created it. Serialization in Java refers to the process of encoding/decoding an object's state as a byte stream.
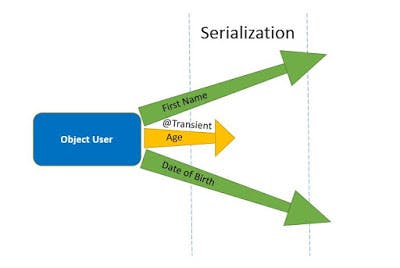
transient keyword provides the required control over serialization process and offers the flexibility to exclude fields when the object is converted to a byte stream. Howvever JPA considers such transient fields as ones having @Transient annotation, hence the field will not be be persisted by JPA as well.
Fields annotated @Transient are converted to a byte stream when the object is serialized, However it will not be persisted by JPA.
@Transient annotation finds its use in modern world of distrubted applications where a field might be of utmost importance for distributed components but at the same time have no business value from persistence per se.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
@Entity
public class User implements Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID \= 1L;
String firstName;
String lastName;
Date dateOfBirth;
@Transient
int age;
}
In the above example we have annotated age field as @Transient. Age field doesnt make sense to be persisted as it must be always calculated based on dateOfBirth field.